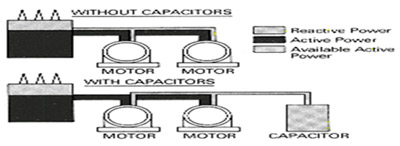
If the power factor of the system is low, improvement or correction of power factor is necessary. Adjusting the power factor of the system closer to unity using some equipment is known as power-factor improvement or correction.Power factor improvement or correction reduces the apparent power consumed by the load and hence, the current drawn by the load will decreases. In other words, power factor correction or improvement is the injuction of reactive power into the circuit to neutralize the effect of lagging current. Static capacitors or synchronous condensers or phase advancers are used to improve or correct the power factor of the system.
Using Static Capacitors :
Static capacitors, whose ratings vary from 15 kVAR to 10000 kVAR, are used as devices to improve or correct power factor of the system. In a three- phase system, the capacitors arranged in star or delta connection arc used to improve the power factor.
Advantages of Static Capacitors:
- Simplest method of power factor improvement or correction.
- Maintenance required in the system is less.
- Easier installation and less weight.
Disadvantages of Static Capacitors:
- Life span of capacitor is short i.e.,8-10 years.
- Gets easily damaged due to over voltages.
- Once the capacitor is damaged, it is difficult to replace.
- Production of switching surges and harmonics happen due to constant switching.
Applications of Static Capacitors:
Capacitors in the range of a few hundred kVAR are used in industrial distribution circuits; capacitors of 500-3000 KVAR rating are used in small distribution substations and those with larger ratings are used in large substations.
Using Synchronous Condensers:
The working of a synchronous motor can be varied, based on the excitation given to its windings. The excitation to the winding is classified as over-excitation, under-excitation and normal-excitation. A synchronous motor in over-excitation and no load condition draws leading current and starts to act like a capacitor and is known as a synchronous condenser. Varying the field excitation can control the amount of kVAR supplied to the load using synchronous condensers.
Advantages of Synchronous Condensers:
- Life span of the equipment is longer i.e.,almost 25 years.
- Power factor control is fexible and reliable.
- Harmonics have no effects on synchronous condensers , as ther is no switiching mechanism.
Disadvantages of Synchronous Condensers:
- Losses in the synchronous condensers are high.
- They are expensive and have a high maintenance cost.
- The noise generated by them pollutes the environment.
- Auxilliary device is required , as a synchronous condenser is not self- starting.
- Use synchronous condenser is uneconomical for equipmnt below 500 kVA.
Applications of Synchronous Condensers:
Synchronous condensers are used in large factories, industries and large substations to improve the power factor and voltage regulation.
Using Phase Advancers:
In a induction motor, the power factor is low, as the stator winding draws lagging current from the supply. Phase advancer, which can be used only in induction motors to improve the power factor, ia a simple AC exciter. It is mounted on the shaft of the induction motor and is connected to the rotor circuit. Phase advancer supplies exciting ampere-turns to the rotor circuit of induction motor at slip frequency, which improves the power factor of the induction motor.