what is the full meaning of HT and LT
Full form of HT & LT
'
HT - High Tension
LT - Low Tension
EHT - Extra High Voltage
Tension is the French Language and the equivalent English translation is Voltage
LT - Low Tension ( Low Voltage )
Low tension lines have low voltage less than 1000 volts and high current distribution system Example of 440V 3 phase supply and 230v Single phase supply.commonly we used LT in Secondary distribution system like our household applications are working in LT. It is used to transmit power at very small distances and use thicker conductor.
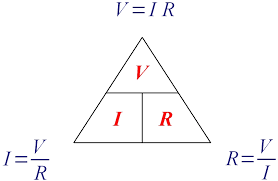
( P= VX I )
Here Low voltage and higher current , conductor size depending up on current.
HT - High Tension ( High voltage )
High Tension lines are using higher voltages ( 11kV, 33kV, ) it is used to Distribute power to large distances by in creasing voltage and decreasing current so as to reduce I^2 R losses. HT line uses thinner conductors than LT line conductor.
EHV - Extra High Voltage
Extra High voltages are using much higher voltages ( above 33 kV to 700 kV ) It is used in Transmission system to transmit higher power.